WSL Mirrored Network Mode Configuration Guide
WSL 2.6.0 networking upgrade configuration guide
Categories:
Version Requirements
Current version status:
- Latest stable: 2.5.9 (known networking issues)
- Recommended version: 2.6.0 preview (full mirrored mode support)
Mode Comparison Analysis
| Feature | bridge mode (deprecated) | mirrored mode (recommended) |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol architecture | Dual-stack | Shared stack |
| IP address allocation | Independent IP (Windows + WSL) | Shared host IP |
| Port resources | Separate | Shared ports (conflict-avoidance required) |
| Network performance | Relatively heavy | Lightweight & efficient |
| Configuration complexity | Simple | Requires deep firewall policy setup |
Standard Configuration Steps
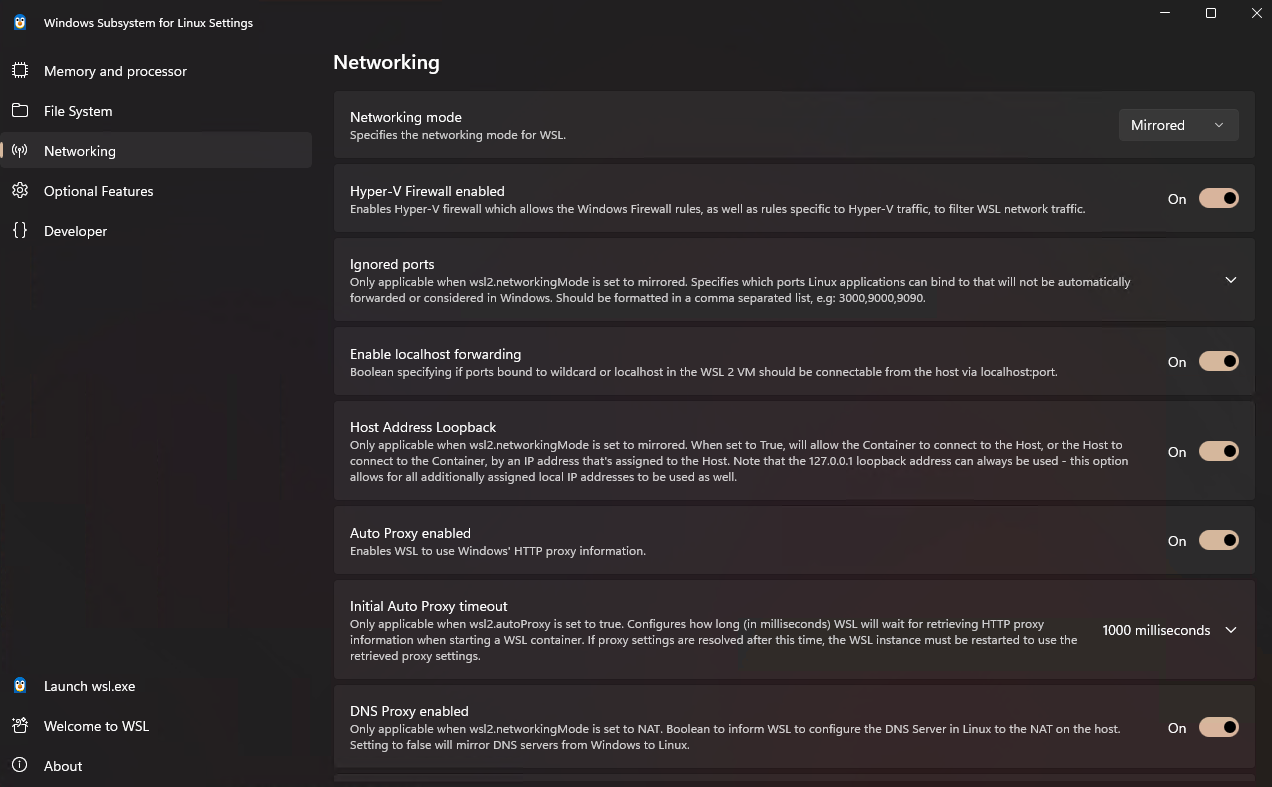
1. Network Mode Settings
Configure the base mode via WSL Settings app:
- Open the Settings app
- Select the Network tab
- Set network mode to Mirrored
- Apply the configuration and restart WSL
2. Firewall Policy Configuration
Run the complete policy configuration via PowerShell:
# Define the WSL VM GUID
$wslGuid = '{40E0AC32-46A5-438A-A0B2-2B479E8F2E90}'
# Configure firewall policies (execute in order)
Set-NetFirewallHyperVVMSetting -Name $wslGuid -Enabled True
Set-NetFirewallHyperVVMSetting -Name $wslGuid -DefaultInboundAction Allow
Set-NetFirewallHyperVVMSetting -Name $wslGuid -DefaultOutboundAction Allow
Set-NetFirewallHyperVVMSetting -Name $wslGuid -LoopbackEnabled True
Set-NetFirewallHyperVVMSetting -Name $wslGuid -AllowHostPolicyMerge True
# Verify configuration results
Get-NetFirewallHyperVVMSetting -Name $wslGuid
3. Port Mapping Validation
# Example: Check port 80 usage
Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 80
Common Issue Troubleshooting
Issue 1: External Connections Fail
- Check step: All fields returned by
Get-NetFirewallHyperVVMSettingshould be True/Allow - Solution: Re-run the firewall policy configuration commands in order
Issue 2: Port Conflicts
- Check method: Use
netstat -anoto view port usage - Handling advice: Prefer to release ports occupied by Windows, or change the listening port in the WSL service
Validation Steps
- Start your WSL service (e.g., Nginx/Apache)
- Access from Windows host:
http://localhost:<port> - Access from LAN devices:
http://<host-ip>:<port>